Types of Farming
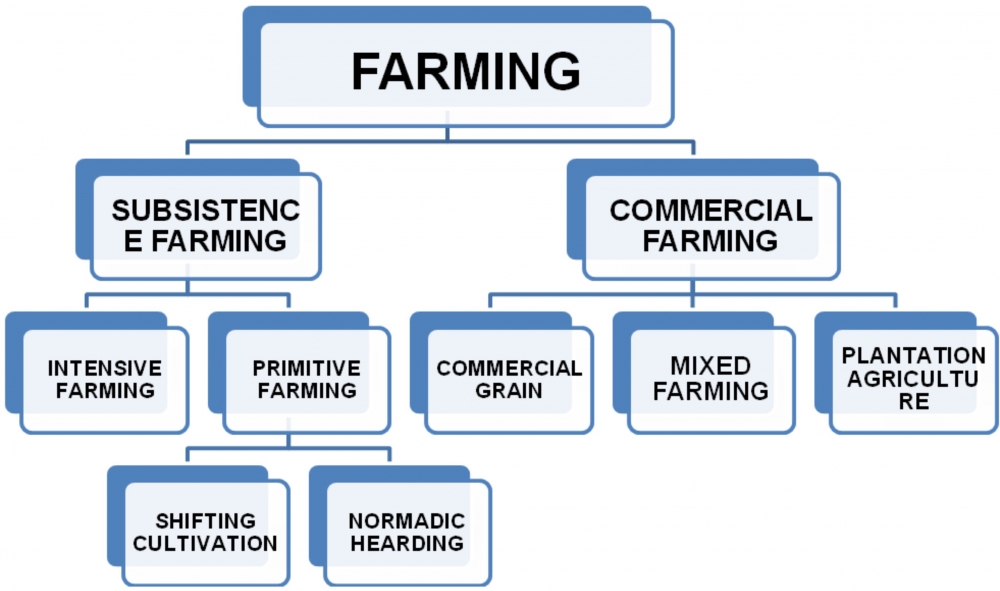
Introduction Farming has been the backbone of human development since ancient times. Different regions practice different types of farming depending on climate, soil quality, culture, and technological development. Whether it’s for personal consumption or large-scale production for global markets, farming helps feed the world and supports the economy. Understanding these types of farming allows us to appreciate how food is produced and how agricultural systems sustain communities worldwide. 1. Subsistence Farming Subsistence farming involves growing crops primarily for household consumption rather than commercial sale. Farmers use simple tools and traditional methods. Features: Best for: Rural families seeking self-sufficiency. 2. Commercial Farming Commercial farming focuses on growing crops and livestock for market sale. It is one of the most advanced types of farming due to technology use. Common Commercial Crops: Advantages: 3. Intensive Farming Intensive farming aims to maximize production from small plots of land through heavy input use. Characteristics: Note: Can affect soil health if not managed sustainably. 4. Extensive Farming Extensive farming uses large land areas with minimal labor and capital. Seen In: USA, Russia, Canada, Australia Key Points: 5. Organic Farming Organic farming avoids chemical fertilizers and synthetic pesticides. This is one of the most environmentally friendly types of farming. Benefits: Challenge: Lower yield and higher cost. 6. Mixed Farming Mixed farming combines crop cultivation and livestock rearing on the same farm. Benefits: 7. Plantation Farming Plantation farming focuses on large-scale production of a single commercial crop. Examples: Often located in tropical regions and require a large labor force. 8. Shifting Cultivation Shifting cultivation is a traditional farming method where land is cleared, farmed for a few years, and then abandoned to recover. However, due to deforestation and environmental laws, this type of farming is declining. 9. Nomadic Herding Nomadic herders move from place to place with their animals in search of pasture and water. Practiced In: 10. Urban and Modern Farming Modern challenges require innovative methods such as: These modern types of farming save space, reduce water usage, and support sustainable living in cities. Sustainable Farming Practices To protect the future, sustainable agriculture promotes: These practices maintain soil fertility and conserve resources. ✅ Conclusion (Enhanced) Farming is not just a profession — it is the foundation of life. The world uses many types of farming, each adapted to different needs, environments, and goals. From village-level subsistence farming to technology-driven commercial agriculture, every method plays a significant role in feeding populations and sustaining economies. As the global population increases, the future of farming depends on innovation and sustainability. Modern technologies like smart irrigation, vertical farming, AI crop monitoring, and climate-resilient seeds will help ensure that agriculture continues to thrive without harming the planet. Supporting farmers, choosing sustainably grown products, and encouraging eco-friendly farming practices are steps toward ensuring a healthy and food-secure future for all. FAQs 1. Which type of farming is best for beginners?Subsistence and organic farming are ideal for beginners due to low risk and natural practices. 2. What farming method is most profitable?Commercial farming and plantation farming offer high profit when managed efficiently. 3. How is organic farming different?It uses natural fertilizers and avoids chemicals to produce healthier food. 4. What is the role of technology in farming?Technology improves crop monitoring, irrigation, and overall productivity. 5. Which type of farming is most sustainable?Organic and mixed farming are considered more eco-friendly.