Introduction to Farming
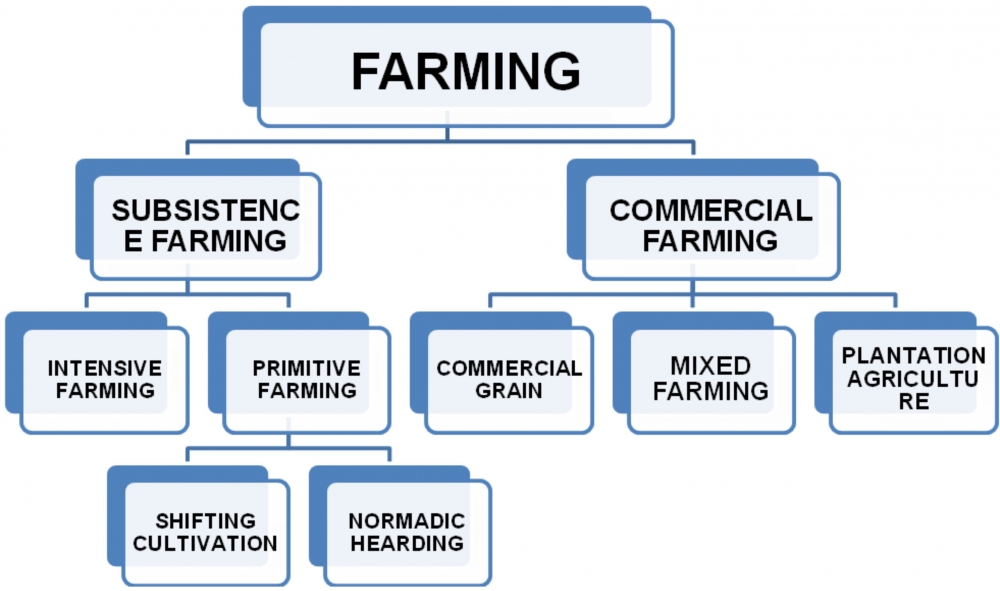
Farming is one of the oldest occupations known to humankind. you know how many types of farming From the earliest civilizations along river valleys to the modern global marketplace, farming has always played a crucial role in feeding populations and shaping societies. Simply put, farming refers to the cultivation of plants and the rearing of animals for food, clothing, medicine, and various industrial uses.
In today’s world, farming isn’t just about growing crops — it’s about using science, technology, and land wisely to produce food efficiently and sustainably. Understanding the different types of farming helps us appreciate how food is produced in various parts of the world.
In today’s world, farming isn’t just about growing crops — it’s about using science, technology, and land wisely to produce food efficiently and sustainably. Understanding the different types of farming helps us appreciate how food is produced in various parts of the world.
Subsistence Farming

This is one of the oldest types of farming practiced worldwide. The main purpose here is to produce food mainly for the farmer and their family rather than for sale.
Commercial Farming

Commercial farming focuses on producing crops and livestock for sale in the market. This is a major part of modern types of farming, especially in developed and industrial countries.
Key examples:
- Wheat
- Coffee
- Cotton
- Sugarcane
Intensive Farming

Intensive farming uses a high amount of labor and investment on a small piece of land to get maximum production. This type of farming is common where population density is high.
This is the opposite of intensive farming. It uses large land areas with minimal labor and capital input.
Extensive Farming
Organic farming avoids chemical fertilizers and synthetic pesticides. This farming method is becoming one of the most popular types of farming because of increasing health awareness.

Benefits:
- Better soil health
- Safer for consumers
- Environmentally sustainable
Mixed Farming
Mixed farming combines growing crops and raising livestock together. This helps improve income stability and soil fertility. Many regions adopt this type of farming to ensure better resource utilization.
Plantation Farming

Plantation farming focuses on growing a single crop over large land areas. It often requires a large workforce and is mostly export-oriented.
Shifting Cultivation & Nomadic Herding
These are traditional types of farming seen in tribal or rural regions. While they have cultural significance, they are decreasing due to modernization and environmental regulations.

Urban & Smart Farming (Future of Agriculture)
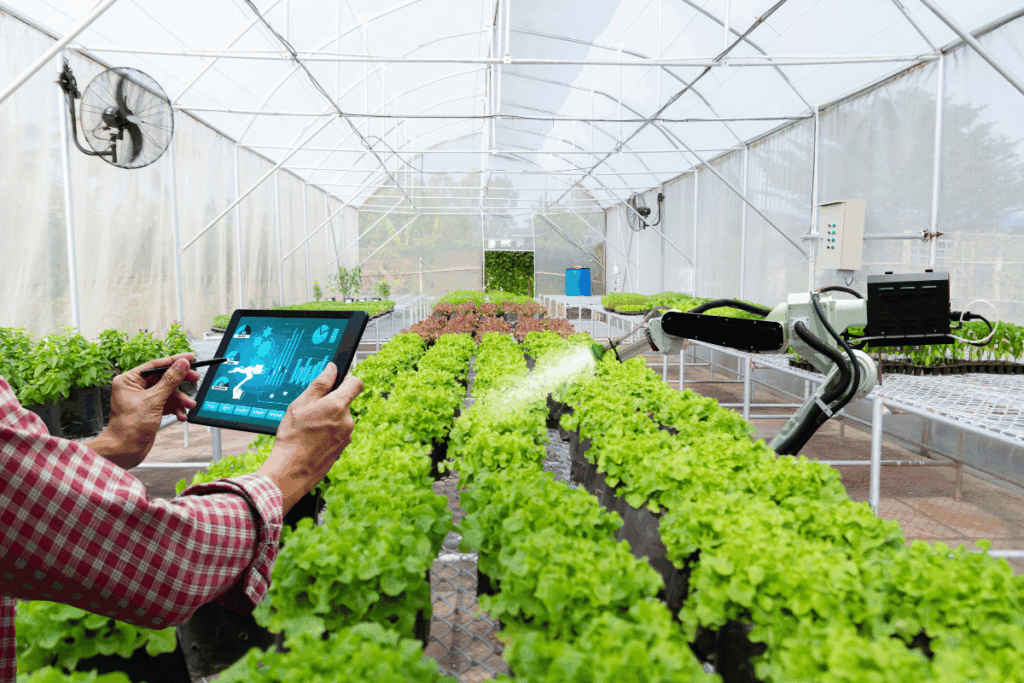

As cities grow, new types of farming such as hydroponic farming, rooftop farming, and vertical farming are being used. These methods save space and resources and support sustainable food production.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of farming gives us a clearer picture of how agriculture works in various parts of the world. Each farming method has developed based on climate, land availability, cultural traditions, and economic needs. Subsistence farming continues to support millions of rural households, while commercial and plantation farming drive large-scale markets and global trade. Mixed farming balances crop production and livestock rearing, while organic farming promotes a healthier and more environmentally friendly way of producing food.
As populations grow and climate change affects weather patterns, farmers face new challenges that require innovative solutions. This is where modern techniques such as smart farming, hydroponics, and sustainable agricultural practices come into play. These new methods help conserve water, reduce chemical usage, increase efficiency, and improve crop resilience.
Ultimately, farming is not just an occupation — it is the foundation of life. Every meal we eat, every grain we cook, and every fruit we enjoy comes from someone’s effort in the fields. Whether traditional or modern, small-scale or commercial, the goal of all farming remains the same:
to nourish humanity and protect the earth for future generations.
By respecting farmers, supporting sustainable practices, and promoting innovation in agriculture, we help build a future where food is abundant, healthy, and accessible to all.
FAQs
1. What is the main purpose of subsistence farming?
To produce food for the farmer’s own household.
2. Which type of farming uses no chemicals?
Organic farming.
3. What is plantation farming known for?
Growing a single crop over large land areas for commercial purposes.
4. Which farming is commonly seen in urban areas?
Rooftop farming and vertical farming.
5. Why are modern farming techniques important?
They improve productivity while reducing labor and time.

